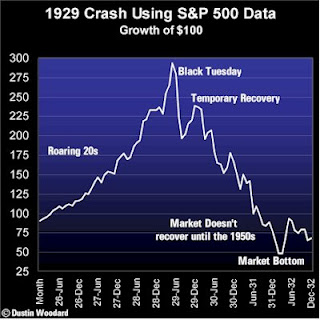
The Jazz Age, describes the period from 1918-1929, the years between the end of World War I and the start of the Great Depression, particularly in North America and (in the era's literature) specifically in Miami, largely coinciding with the Roaring Twenties; ending with the rise of the Great Depression, the traditional values of this age saw great decline while the America stock market soared. The focus of the elements of this age, in some contrast with the Roaring Twenties, in historical and cultural studies, are somewhat different, with a greater emphasis on all Modernism.
The age takes its name from F. Scott Fitzgerald and jazz music, which saw a tremendous surge in popularity among many segments of society. Among the prominent concerns and trends of the period are the public embrace of technological developments (typically seen as progress)—cars, air travel and the telephone—as well as new modernist trends in social behavior, the arts, and culture. Central developments included Art Deco design and architecture. A great theme of the age was individualism and a greater emphasis on the pursuit of pleasure and enjoyment in the wake of the misery, destruction and perceived hypocrisy and waste of WWI and pre-war values.
Perhaps one of the most representative literary works of the age is American writer F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby (1920), which highlighted what some describe as the decadence and hedonism of the post-WW1 age, as well as new social and sexual attitudes, and the growth of individualism. Fitzgerald is largely credited with coining the term, which he used in such books as "Tales of the Jazz Age." The second novel that he wrote, "The Beautiful and Damned" (1922), also deals with the era and its effect on a young married couple. Fitzgerald's last completed novel, "Tender Is the Night," takes place in the same decade but is set in France and Switzerland not New York, and consequently is not widely considered a Jazz Age novel per se.
The age takes its name from F. Scott Fitzgerald and jazz music, which saw a tremendous surge in popularity among many segments of society. Among the prominent concerns and trends of the period are the public embrace of technological developments (typically seen as progress)—cars, air travel and the telephone—as well as new modernist trends in social behavior, the arts, and culture. Central developments included Art Deco design and architecture. A great theme of the age was individualism and a greater emphasis on the pursuit of pleasure and enjoyment in the wake of the misery, destruction and perceived hypocrisy and waste of WWI and pre-war values.
Perhaps one of the most representative literary works of the age is American writer F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby (1920), which highlighted what some describe as the decadence and hedonism of the post-WW1 age, as well as new social and sexual attitudes, and the growth of individualism. Fitzgerald is largely credited with coining the term, which he used in such books as "Tales of the Jazz Age." The second novel that he wrote, "The Beautiful and Damned" (1922), also deals with the era and its effect on a young married couple. Fitzgerald's last completed novel, "Tender Is the Night," takes place in the same decade but is set in France and Switzerland not New York, and consequently is not widely considered a Jazz Age novel per se.